What is RDIMM?
Registered DIMM (RDIMM) is a type of memory module that includes a register between the memory chips and the memory controller. This register helps to reduce the electrical load on the memory controller, allowing for more memory modules to be used in a system without compromising stability. RDIMMs are commonly used in servers and workstations due to their ability to support larger memory capacities and improve performance in multi-module configurations
New Technology in OC RDIMM (Overclock Registered DIMM)
OC RDIMMs is designed for high-performance computing environments where speed is crucial. They allow users to push the memory beyond standard specifications, providing enhanced performance for demanding applications.
Key Features of OC RDIMMs:
- Higher Speeds: OC RDIMMs can operate at significantly higher frequencies (e.g., 4800 MHz to 8000 MHz), improving data transfer rates.
- Enhanced Stability:Despite the overclocking, these modules are engineered to maintain stability under high-performance conditions.
- Compatibility: Designed to work with specific motherboards and processors that support overclocking.
Why Upgrade to OC RDIMM for Your Workstation or Server?
Upgrading to OC RDIMMs can provide several advantages for your workstation or server:
- Improved Performance:
Higher memory speeds lead to faster data processing, which is beneficial for tasks such as video editing, 3D rendering, and large database management. - Increased Efficiency:
Enhanced memory performance can reduce bottlenecks, allowing the CPU to operate more efficiently and improving overall system responsiveness. - Future-Proofing:
As applications become more demanding, having OC RDIMMs can help ensure your system remains capable ofhandling future workloads. - Better Multitasking:
With increased memory bandwidth, OC RDIMMs allows for smoother multitasking, enabling users to run multiple applications simultaneously without performance degradation.
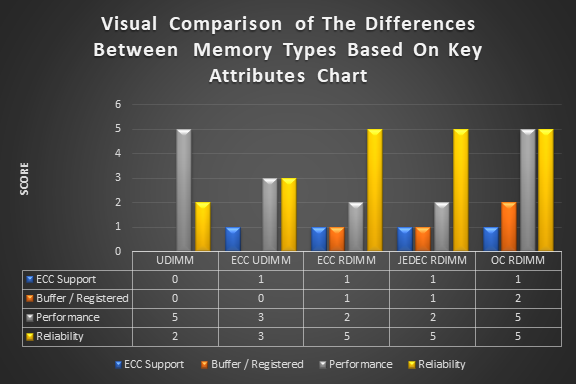
Differences Between UDIMM, ECC RDIMM, and RDIM
- UDIMM (Unbuffered DIMM):
Definition: A standard memory module without a register.
Use Case: Typically used in consumer desktops and laptops.
Capacity: Generally, supports lower memory capacities compared to RDIMMs.
Performance: Offers lower latency and higher speeds but is less stable with multiple modules. - ECC RDIMM (Error-Correcting Code Registered DIMM):
Definition: A type of RDIMM that includes error-correcting code functionality.
Use Case: Commonly used in servers where data integrity is critical.
Error Correction: Can detect and correct single-bit memory errors, enhancing reliability.
Performance: Slightly higher latency than standard RDIMMs due to error correction processes. - RDIMM
Definition: Registered DIMM without error correction.
Use Case: Used in enterprise environments where stability and capacity are prioritized.
Capacity: Supports higher memory capacities than UDIMMs.
Performance: Higher latency compared to UDIMMs but better suited for multi-module configurations.
.png)
Understanding the differences between RDIMMs, UDIMMs, and ECC RDIMMs is crucial for selecting the right memory for your needs. Upgrading to OC RDIMMs can significantly enhance the performance of your workstation or server, making it a worthwhile investment for users requiring high-speed and reliable memory solutions.
Applications in Workstations and Servers
RDIMM, OC RDIMM, and DDR5 memory are critical components in modern workstations and servers, designed to meet the demanding needs of professionals.
- Workstations
Graphic Design and CAD: High-capacity RDIMM ensures smooth rendering and modeling.
Video Editing: DDR5’s high bandwidth accelerates video encoding and playback.
AI and Machine Learning: RDIMM’s stability supports large datasets and intensive computations.
- Servers
Data Centers: RDIMM’s scalability and error correction ensure consistent uptime.
Virtualization: Supports multiple virtual machines with high memory demands.
High-Performance Computing (HPC): DDR5’s speed and capacity enable complex simulations and analyses.
























